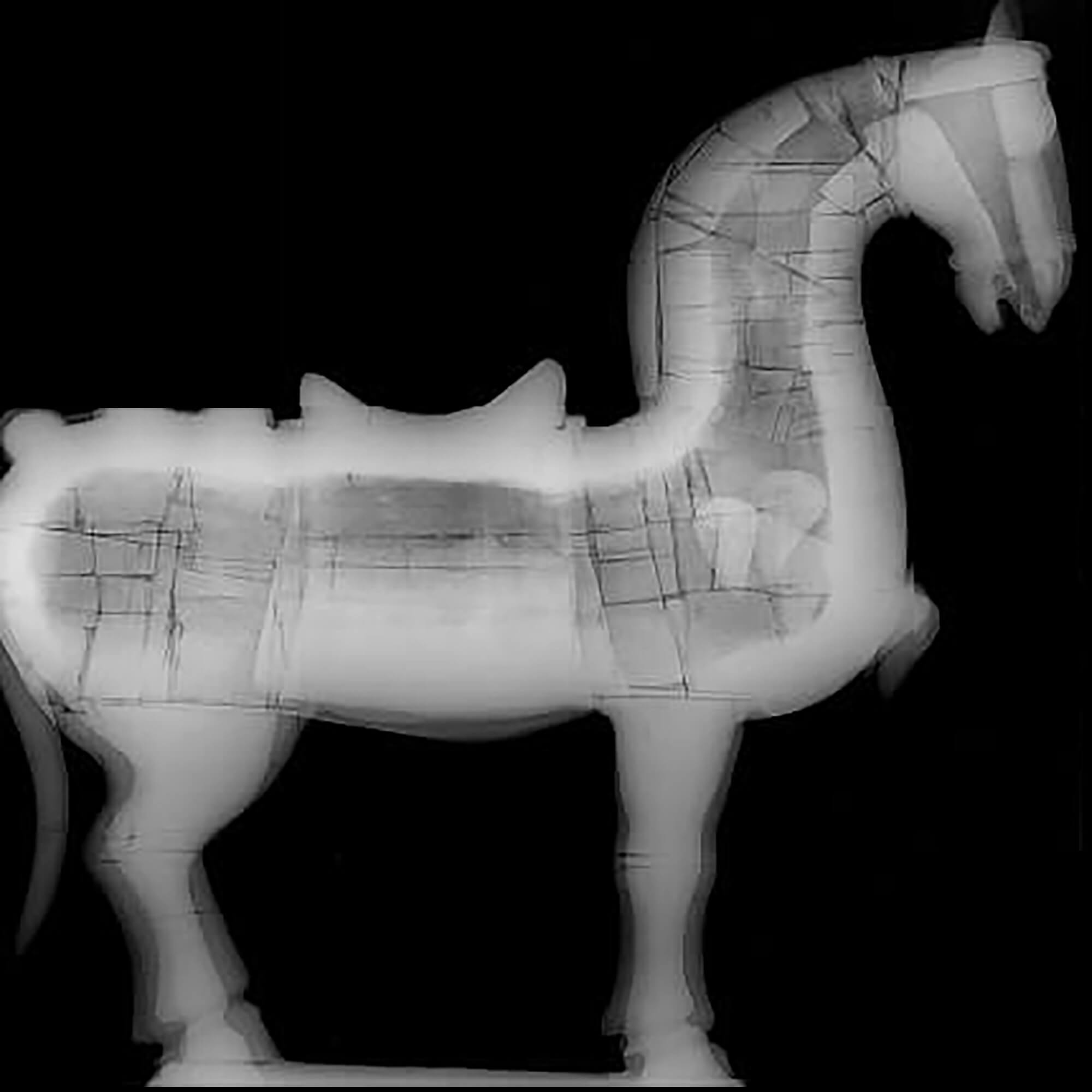
Comparison between carbon-14, TL, and OSL: which method should you choose?
Choosing the right dating method in archaeology is not just a technical issue: it is a key decision that guides the entire interpretation of a site. Which technique to choose...