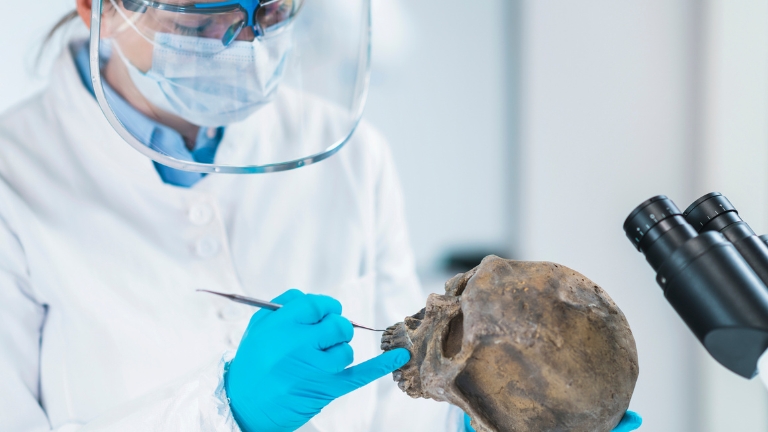
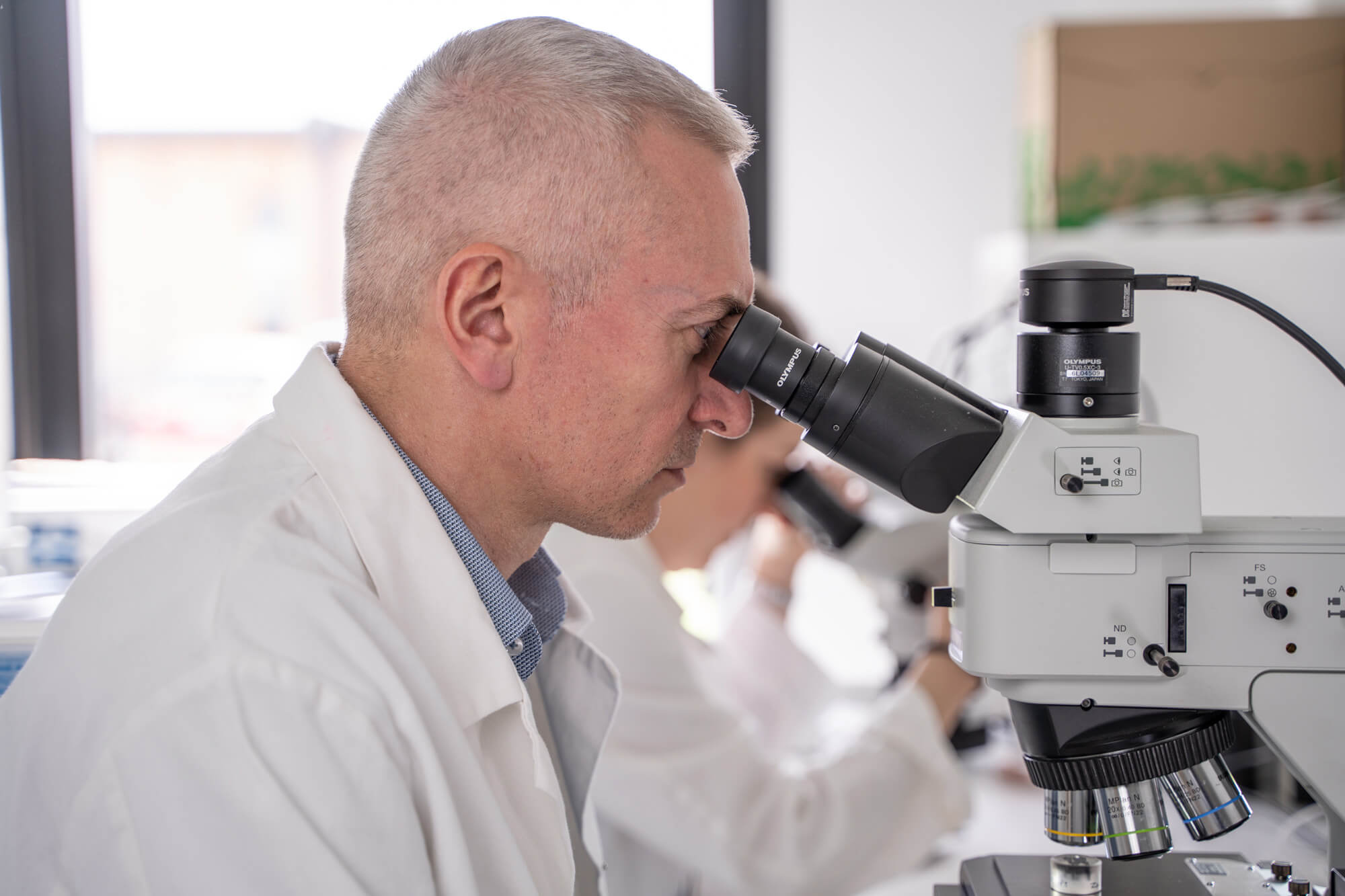
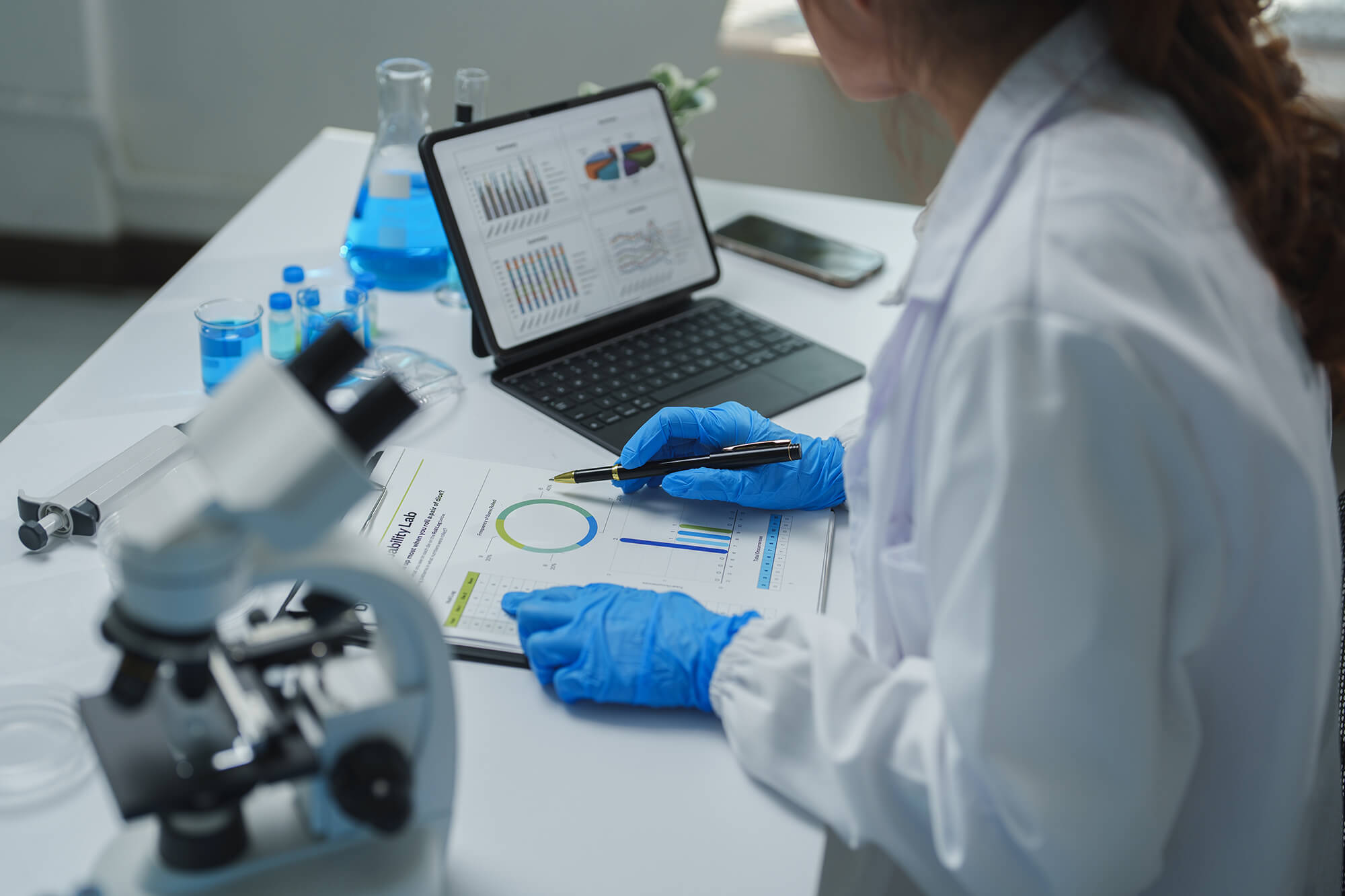
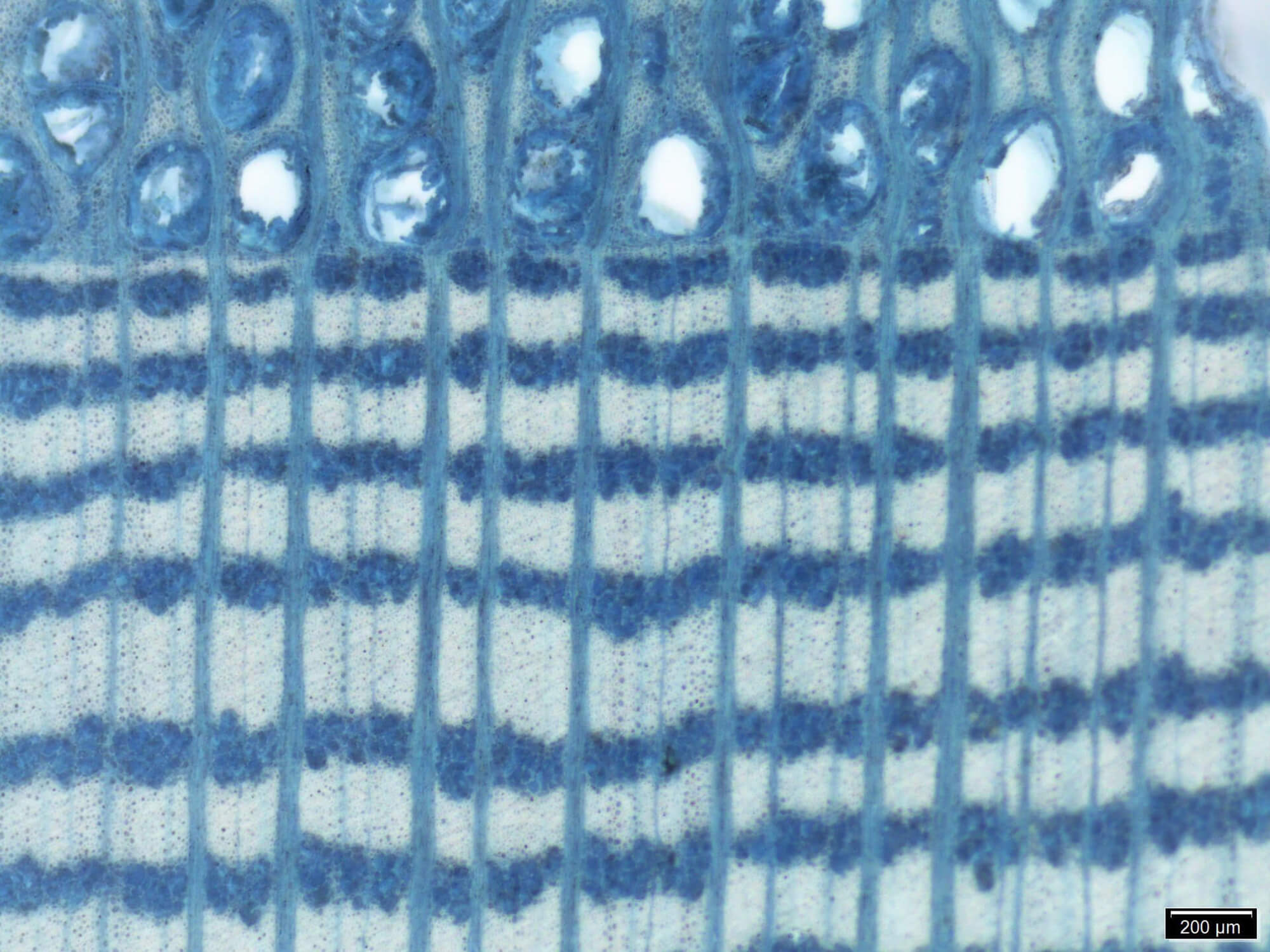
CIRAM, laboratories for the analysis of archaeological artefacts
CIRAM laboratories offer advanced analyses in anthracology, xylology and dendrochronology, as well as complementary services such as carbon-14 dating, organic residue analysisanalysis luminescence dating and isotope analysis.
We guarantee reliable results within two to four weeks to meet your requirements for preventive archaeological excavations. Thanks to our state-of-the-art equipment and recognized expertise, we support our customers before, during and after sample analysis for accurate, detailed conclusions.
For accurate results from Europe's leading laboratory, request a free quote on our website.
Contact our teams