CIRAM Laboratories,
expert in scientific imaging
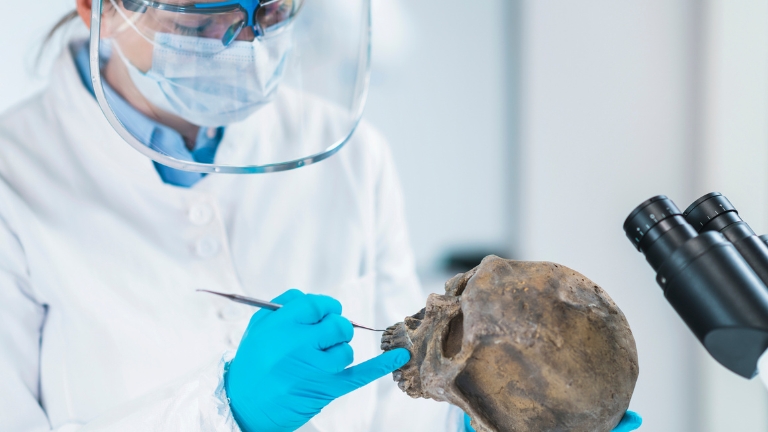
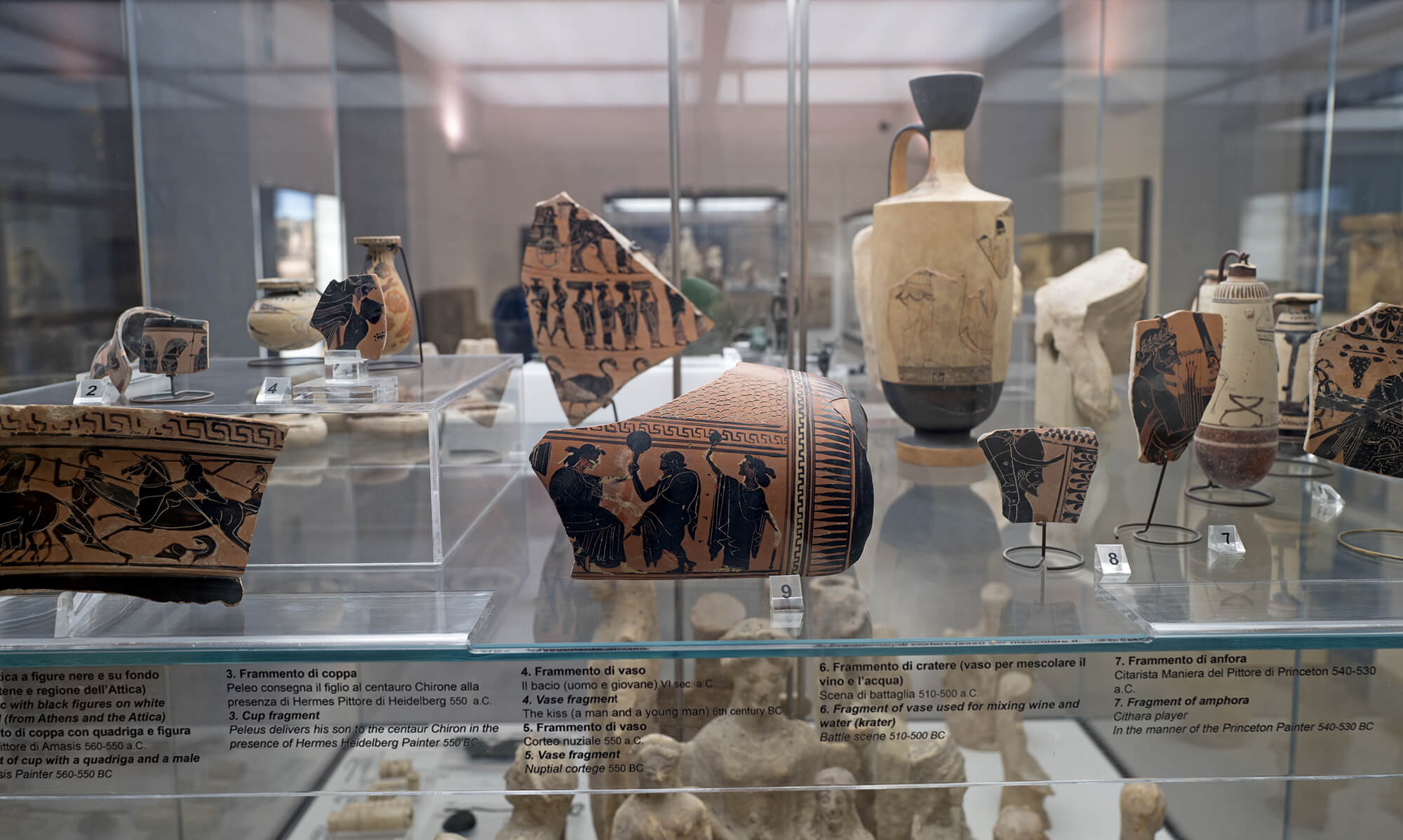
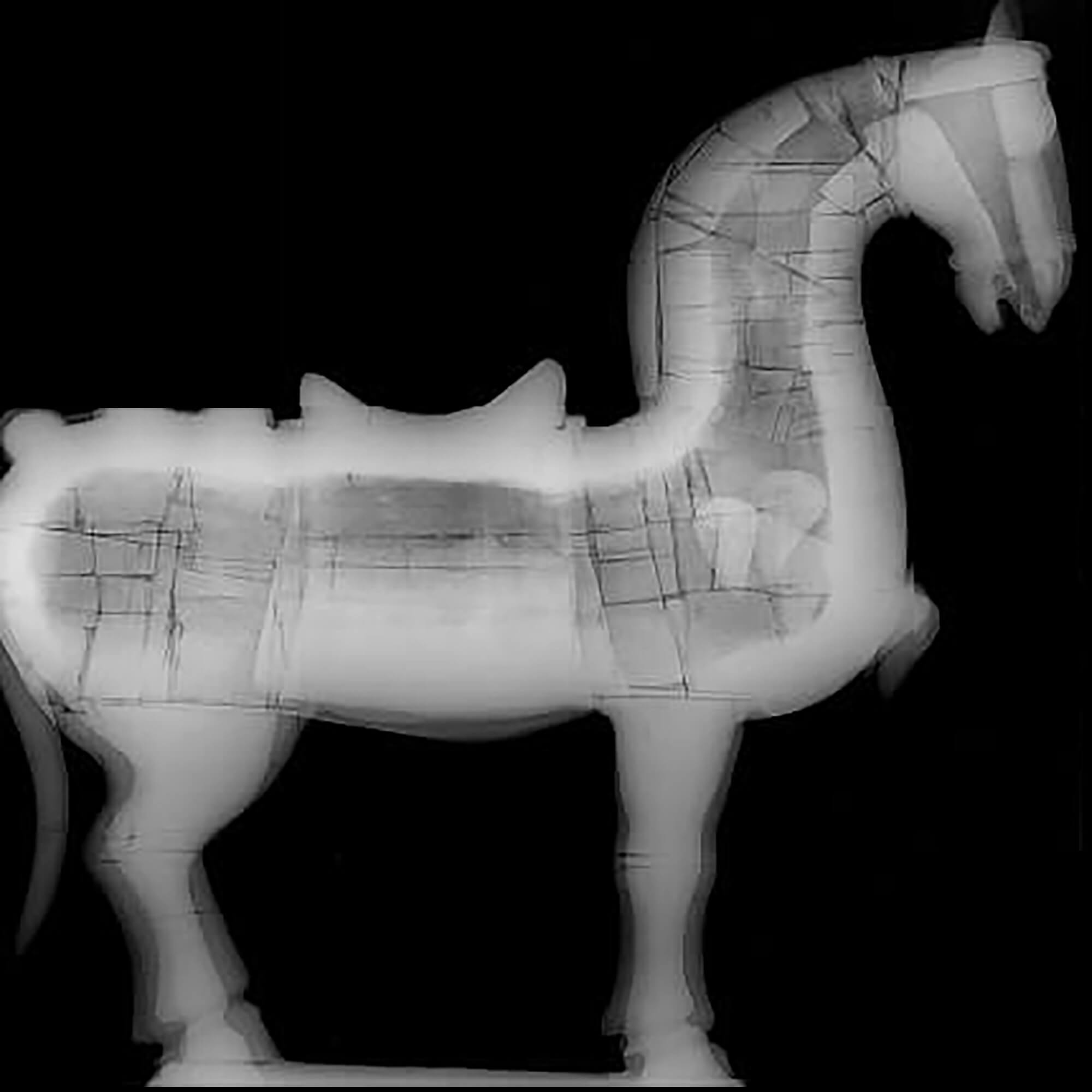
CIRAM laboratories are at the forefront of innovation in the field of scientific imaging applied to archaeology. Thanks to a team of experts and state-of-the-art technologies, CIRAM offers non-destructive imaging solutions for the analysis and conservation of archaeological artifacts.
Combining X-ray and CT scan techniques, CIRAM provides a detailed exploration of objects, from their internal structure to their state of preservation.
These technologies, combined with complementary analyses such as carbon dating by AMScarbon dating thermoluminescence dating, anthracology/xylology, organic residue analysis or isotope analysisanalysis, provide an in-depth understanding of artifacts, while guaranteeing their preservation.
Contact our teams